Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
🔐 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Why You Need It
Even the strongest passwords can be stolen through phishing, malware, data breaches, or simple guessing.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a critical layer of security that blocks attackers even if they have your password.
If you’re learning the basics of digital protection, you may want to browse our broader Cyber & Digital Security section for related topics.
🧭 What Is MFA?
MFA requires you to prove your identity using two or more categories:
- Something you know — a password or PIN
- Something you have — a phone, app, hardware key
- Something you are — fingerprint, face ID
So even if someone steals your password, they can’t access your account without the second factor.
This protects you from phishing attacks described in our Social Engineering guide.
❓ Why MFA Is So Important
Most account breaches happen because:
- Passwords are weak
- Passwords are reused across multiple sites
- Passwords were exposed in a data breach
- Users clicked a phishing link
- Malware stole login credentials
MFA stops the majority of these attacks.
Even if attackers know your password, they’ll still need:
- Your phone
- Your authenticator app
- Your hardware key
…which they don’t have.
To learn more about password safety, see our guide on creating Strong Passwords.
🔍 Common Types of MFA
1️⃣ One-Time Codes (SMS or Email)
You receive a short code you must enter to log in.
Pros: Simple, widely available
Cons: Vulnerable to SIM swapping and phishing
2️⃣ Authenticator Apps (Recommended)
Apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy generate secure rotating codes.
Pros:
- More secure than SMS
- Works offline
- Harder to intercept
This is the most common and recommended method for everyday users.
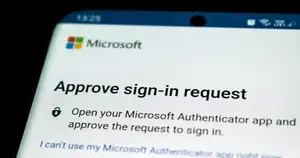
3️⃣ Push Notifications
Your phone receives a notification asking you to approve or deny a login attempt.
Pros: Fast and user-friendly
Cons: Can be abused with “push bombing” (attackers send repeated prompts)
4️⃣ Hardware Security Keys (Most Secure)
Devices like YubiKey or FIDO2 keys require a physical tap to confirm login.
Pros:
- Nearly impossible to hack remotely
- Protects against phishing entirely
Cons:
- Requires a physical device
These are especially useful for high-risk users and professionals handling sensitive information.
🛠️ How to Enable MFA (General Steps)
1️⃣ Go to Your Account Settings
Look for options like:
- “Security”
- “Login & Security”
- “Account Protection”
2️⃣ Find Multi-Factor or Two-Step Verification
Names vary:
- MFA
- 2FA
- Two-Step Verification
- Login Security
3️⃣ Choose an Authentication Method
Preferably:
Authenticator App → Hardware Key → SMS (in that order of security)
4️⃣ Scan the QR Code or Enter the Setup Key
Your authenticator app will begin generating codes.
5️⃣ Save Backup Codes
Backup codes let you access your account if you lose your phone.
Store them safely — not in your email inbox or notes app.
🧠 Additional Tips for Strong MFA Usage
✔ Avoid SMS When Possible
SMS can be intercepted or redirected by attackers.
Use it only if no other option is available.
✔ Protect Your Email First
Your email is the “master key” to all your accounts.
Enable MFA on your email before anything else.
✔ Watch for MFA Fatigue Attacks
If you receive repeated login approval requests you didn’t initiate, decline them.
This tactic is often used in targeted attacks.
✔ Use Hardware Keys for Sensitive Accounts
If you use banking apps, manage crypto, or run a business, hardware keys offer elite-level protection.
🛡️ How MFA Helps Against Real Attacks
MFA prevents:
- Password stuffing
- Credential leaks
- Data breaches
- Phishing-based login theft
- Remote account access
- Basic malware credential theft
To understand how malware steals passwords, see our guide on Malware & System Defense.
📚 Summary
MFA is one of the simplest and most effective ways to secure your accounts.
It adds a second barrier that stops attackers even if they somehow obtain your password.
To continue improving your online security, explore: